Erosion is the process when things breaks down or displacement of solids by agents such as wind, water or even animals. Therefore erosion is all around us, but let us discuss about how the surface of the earth is affected by erosion along the coast line or Coastal Erosion
 Coastal Erosion
Coastal ErosionThe coast is a narrow contact between the land sea, and it is constantly changing due to the effects of land, air and marine processes. Most of the erosion on coast are cause by the waves from the sea as you can see from the picture to your left
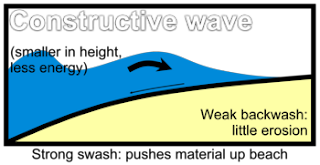
There are two types of waves constructive and destructive. Waves have a circular pattern, but when it reaches the shallow water the bottom come in contact with the surface, this creates friction at the bottom causing the top part to build up, it becomes steeper and higher until it breaks and the water rushes up the the beach called the swash and the backward wash called the backwash. Constructive waves have limited energy. Most of this is used by the swash to transport the material up the beach. Destructive waves have much more energy. Most of this is used by the backwash to transport material down the beach

Now you can see how different types of waves affect the coast, but the coast itself also determines the shape. The coast is made out of rocks, there are soft rocks and hard rocks. When erosion occurs, areas with harder rocks erode slower then the softer rocks creating headlands, and the softer rocks which erode faster forms a bay. Their size depends how much each type of rock is in that area. Hard rocks can be rocks like sand stones, chalk or limestones, and soft rocks can be ricks such as clay.

Cliffs, cliffs tends to form in area of hard, resistant rocks, however there are also weakness within these rocks causing it to erode away forming caves and eventually arches. over time when it can't support anymore it collapses leaving a stack behind and eventually after the stack falls it leaves a stump. In this picture , we can see the arch and
 some stumps left behind. This process continue until it can not erode further or what we call a death cliff.
some stumps left behind. This process continue until it can not erode further or what we call a death cliff.At the bays where there are soft rocks, we usually finds a beach. Beaches are faced with the process called longshore drift. Longshore drift is the process of the material along the coast by breaking waves. The direction of the prevailing wind is at an angle, therefore the wave is also at an angle pushing the sand particle and sediments move diagonally up
 wards and they are push backwards by the backwash. causing a zigzag movement, and eventually it might cause the whole beach to disappear if there are no deposition of particles from other source. This process can be slowed down by placing a wall called a groyne like in the picture
wards and they are push backwards by the backwash. causing a zigzag movement, and eventually it might cause the whole beach to disappear if there are no deposition of particles from other source. This process can be slowed down by placing a wall called a groyne like in the picture
The sediment carried away longshore drift most of the time end out forming a spit on a delta or a river mouth. The spit slows down the velocity of the river creating a salt water marsh
 , if it closest the mouth completely it may result a lagoon. In this diagram the salt water marsh has already formed behind the spit.
, if it closest the mouth completely it may result a lagoon. In this diagram the salt water marsh has already formed behind the spit.After all this how can coastal erosion be hazards, coastal erosion can cost houses or building built on a cliff to completely collapse and another thing is the lost of land, or a country like Britain with coast all around, it is going to lose quite an amount of land. Coastal Erosion can be a few centimeters a year but over time it adds up. There're many schemes that slows down coastal erosion or permanently stop it. Like the groyne above or we can built a sea wall which may be curved at the top to divert the force of the wave back o
 f to sea. We can also dump in rocks to reduce the power of the waves. This picture to you right is an example of seawall and also the wall of rocks before the sea wall to prevent coastal erosion.
f to sea. We can also dump in rocks to reduce the power of the waves. This picture to you right is an example of seawall and also the wall of rocks before the sea wall to prevent coastal erosion.